Carnot Efficiency
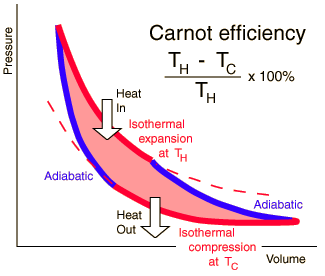 |
The maximum heat that can be converted to mechanical work is fully described by the Carnot efficiency; the ratio of the output work to the input heat of a system. As a percentage of input heat the output work (ηth) can be expressed by the equation below, where Tc = Tl is the temperature of the cold sink and Th is the temperature of the heat source (in Kelvin).
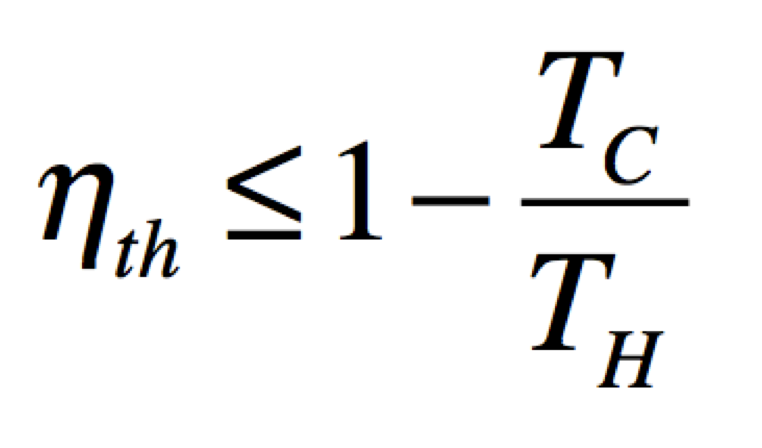
There are many sources of irreversibility which contribute to loss of efficiency.[14] The main contributing sources of irreversibility are: heat flowing directly from the source to the sink; the full temperature gradient may not be available due to thermal resistance across the path of heat flow; some of the work generated is converted back to heat by friction; the expansion may do no work and only increase the entropy (as in the case of expansion into a vacuum, no work is done).